The U.S. Economy Showing Signs of a Slowdown – Again. Here’s What to Watch This Week.
/in Investing/by Tom 2Economics
Last Week
The main takeaway from last week, from a data perspective, is that the slowdown in domestic growth we saw in March is extending into April. Pretty much every data point from last week showed a slowdown in economic activity.
The Empire Manufacturing Survey and Philly Fed Index, two of the first data points from April, both missed expectations, and importantly the New Orders component for both declined, implying more weakness ahead.
The other two big data points of the week, Industrial Production and Housing Starts, also showed some moderation in the pace of growth, despite the headlines for both numbers beating expectations (IP was higher because of utility output, while housing starts beat because of multi-family starts, neither which are really positive).
Finally, jobless claims were “OK” but importantly they have broken the downtrend they were in throughout late February/early March, implying the positive momentum in the jobs market has stalled.
Finally, the most damaging data this week came on Monday, when Chinese GDP missed expectations, and industrial production and retail sales were also weak. Plus, housing prices continued to rise in major metropolitan areas, increasing the likelihood of more measures being announced to curb rising property prices.
Bottom line is that one of the major concerns of the market, and one of the reasons for the fall in equity prices this week, has been the return of another “Spring dip” in economic activity, and data this week only reinforced that fear.
This Week
The focus remains on global economic growth this week and by far the most important numbers will be the Flash Manufacturing PMIs out tonight and tomorrow. Chinese PMI comes tonight and the EU and US figures will be released Tuesday morning.
Even without the PMIs it is a relatively busy week from an economics perspective. The second most important number behind the PMI is Durable Goods, out Wednesday. Retail sales lately have disappointed, implying some softening in consumer spending, so business spending will be closely watched to see if it too is declining.
The first look at Q1 ‘13 GDP is Friday, although this number, which will be good, isn’t quite as important as you would think because the focus now is on the moderation of growth in March and now April (GDP reflects the entire quarter, so Jan/Feb will skew the number higher than what the economy is currently doing).
Weekly jobless claims will be watched to see if the downtrend from February/March can resume, and there’s existing and new home sales (Monday and Wednesday), which will give us a bit more color into the state of the housing market (the numbers should show continued strength in pricing and low inventories).
Internationally, away from the Flash Manufacturing PMIs early in the week, it’s somewhat quiet. There is a Bank of Japan meeting Thursday, but after the “shock and awe” from the April meeting, not much new is expected. UK GDP is released Thursday as well.
Bottom line is that economic growth remains the key issue in markets. The Flash manufacturing PMIs are by far the most important number of the week, and depending how they go, it may well decide whether this correction stalls or accelerates.
Indices to Watch Today – Part II
/in Investing/by Tom 2What Does the Commodity Meltdown Mean?
The declines in gold and silver yesterday were astonishing. In 10+ years of watching both metals trade every day, I’ve never seen that type of decline. In addition to gold and silver collapsing again, every single commodity on my screen was lower, with the exception of orange juice.
This commodity rout is important as it’s the biggest thing occurring in any market right now. I touched on it some yesterday, but I want to review it more in depth today to make sure everyone knows what’s happening and what it means. I believe what’s happening in the commodity space presents a binary outcome for all asset classes, and I want to make sure everyone knows the two ways this is going to work out.
Theory No. 1—The Return of the “Real” Economy.
The first theory is a bullish one: The reasoning goes that gold and silver are declining because we are on the cusp of another period of real economic growth and technological advancement that will see equities rally substantially as the real economy finally kicks into gear after years of stagnation. That expectation is causing a rotation out of inflation and crisis-linked commodities like gold, and into more economically sensitive assets like stocks, which will benefit from the new momentum in the economy.
This theory is certainly possible, but there are a few problems: First, if we are on the cusp of a period of economic advancement, then why are all commodities getting killed, including economically sensitive commodities like oil, copper, steel, gasoline, palladium and others? The answer to that question seems to be increased supply—and that increased supply is causing wholesale rotation out of commodities and into stocks. That is a fair argument and very well may be true.
But, there is one other chink in the armor of Theory No. 1. If we are on the cusp of a new period of economic expansion, then why aren’t bonds falling? Bonds have been rising since March, and if we’re about to see the real economy kick into gear for the first time in 4+ years, bonds should be falling like a stone—but they aren’t. One possible explanation is that money flows from Europe and Japan are holding bonds up, but I haven’t seen enough evidence to tell me that’s the case.
What do we do if this theory is true: You buy U.S. stocks with both hands, and sell any commodity exposure and reduce bond holdings.
How will we know if this is the right theory: You’ll know because 1) bonds will crack, 2) economic data will accelerate, and 3) corporate profits and outlooks will get better (none of which is happening now).
Theory No. 2: The Deflation Theory
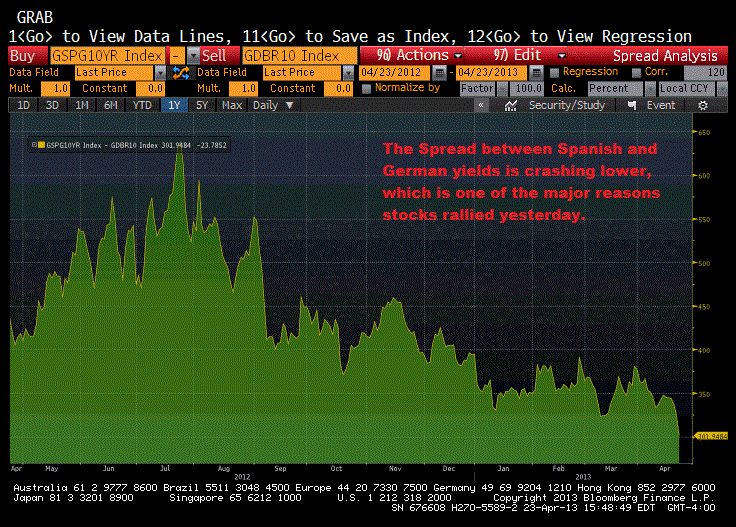
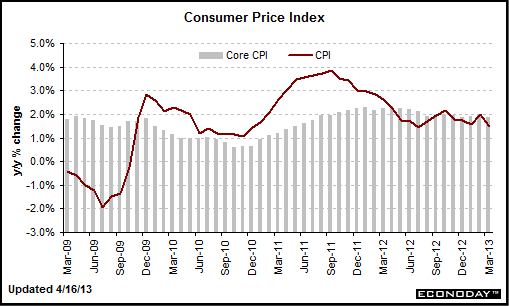
The second theory is a deflation theory. With gold and silver imploding and industrial commodities (in fact all commodities) declining rapidly, and U.S. Treasurys and German Bunds rallying throughout March, markets are telling us the global economy is very close to entering a period of deflation. Europe is dangerously close (if not already in) deflation, Japan is still in deflation, and Chinese and U.S. economic growth is slowing.
The “deflation trade” is occurring in commodities (especially gold and silver) first as money flows out of commodities its flowing into bonds.
This theory also makes sense, except for one thing—the equity market is still rising. Stocks are rallying in the face of a commodity collapse and higher bond prices, and that shouldn’t happen in a deflationary environment.
One possible answer to why this is happening is money flows. Investors are continuing to buy into stocks because they “have to” because of the Fed, which is propping up the stock market despite significantly deteriorating fundamentals.
What do we do if this theory is true: You get defensive. We buy bonds and reduce equity exposure and raise cash, because if this theory is true, stocks are going to fall, and fall very hard.
How will we know if this theory is true: You’ll know because the equity market will break from its highs and bonds will continue to rally to new highs.
I want it to be Theory No. 1, but my gut is afraid it’s Theory No. 2. Not to sound like a loon, but the last time I saw commodity carnage like this was in July/August of 2008. I’m not saying there is going to be another financial crisis (I don’t think there will be) but I’m just pointing it out.
Finally, a lot of markets simply aren’t making sense right now—if we’re in a new golden age of economic expansion why aren’t bonds falling? If we’re in deflation, why aren’t stocks falling? How the hell have bonds and stocks been rising together for the last seven weeks? When things don’t make sense like this, I’ve never seen it end with a melt-up in the market. I hope that this time I’m wrong.
One more thing—if Theory No. 2 is the correct one, I think this ultimately ends with more Fed easing, which will be good for gold, which means that at some point there will be a buying opportunity (I don’t think it’s now, too much technical damage has been done and the commodity needs to settle a bit).
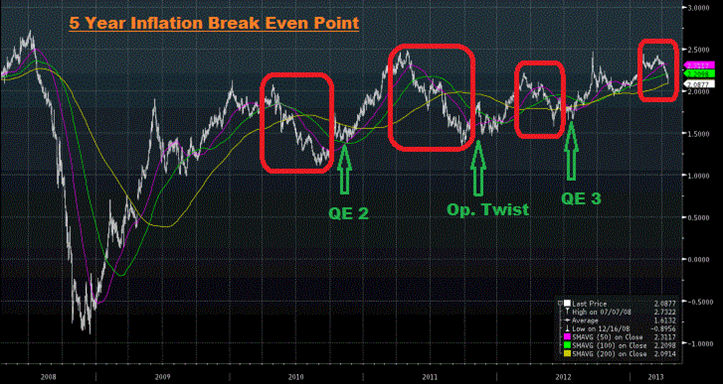
The chart above shows the five-year inflation expectations of the market. As you can see, they’ve declined sharply over the past several weeks. I’ve highlighted previous times the inflation expectations have seen a significant decline, and each time its been met with more Fed easing. If the declines in inflation expectations continue, that means deflation, and the Fed will ease more in the coming months, not tighten. This remains an important indicator to watch.
Commodities in Freefall and What it Means
/in Investing/by Tom 2Commodities
Commodities declined sharply last week, as the broad-based commodity ETF DBC declined more than 1%, with most of the weakness coming on Friday. The ETF and most commodity indices moved to multi-month lows, implying more weakness ahead.
The decline in commodities came despite a weaker dollar and generally “OK” global economic data. Continued rotation out of the commodity space by investors was the main catalyst for the declines.
Gold imploded last week, falling 5% on Friday alone and 6% for the week. The reasons for the weakness in gold are the same as they have been: negative momentum and money rotation out of gold due to a reduction of risk globally and a total lack of inflation (and potential threat of deflation in Europe).
The one main catalyst for Friday’s decline, however, was the report that Cyprus will have to sell some of its gold (or pledge it as collateral against EU loans), which sets a significant precedent and obviously got gold longs very nervous.
Despite a very low speculative net long position and a rising monetary base, money flows are trumping fundamentals and clearly there is very heavy negative momentum in gold. I was very, very surprised by the waterfall decline Friday, and clearly the technical damage done was significant.
What to do with gold now depends on your time horizon. I, for one, continue to see all signs pointing to inflation over the longer term, thanks to continued central bank accommodation and excess liquidity. I’m very confident inflation will be a problem in the future, and as such I would/am not selling longer-term gold holdings. With gold and silver plunging again this morning we are in the midst of a sellers panic at this point, although I’m hearing there is decent support in the mid $1300’s. Silver and copper also declined sharply last Friday and this morning in sympathy with gold, and both finished lower on the week (with silver hitting new 52-week lows).
Energy declined last week as WTI Crude broke through support at the $91/bbl. level and Brent crude fell basically to previous lows for the year. Both commodities were pressured by general commodity market weakness.
Finally, grain markets were the outperformers last week as the entire complex rallied, bouncing from an oversold condition after a USDA World Agricultural Supply/Demand Estimate report showed that the supply of corn and soybeans hadn’t grown as much as thought (the report wasn’t bullish, it just wasn’t as bearish as feared). Given the number of shorts in the grains, that led to a short covering rally, although the supply/demand picture remains uncertain and given the planting intentions for this year, it’s not certain that you’re buying “value” in the grains at these levels.
The weakness in the commodity markets remains an important topic to monitor. On one hand, you can make the case the decline is justified, given recent supply increases in commodities like copper, WTI Crude and steel. But, while those supply increases are totally legitimate, they are overshadowing the weakness in the global economy, which is something I think needs to be considered.
Commodities as an asset class are signaling one of two things: 1) That we are returning to a period like the 1980s where increased supply, reduced macroeconomic uncertainty and low inflation depresses commodity prices, and we see a renewed equity bull market where stocks significantly outperform commodities. Or, 2) the weakness in commodities is signaling trouble on the macroeconomic horizon, as global growth stagnates and we all flirt with another bout of global deflation (which would better explain gold’s weakness than just money flows). Scenario No. 1 is equity market positive, scenario No. 2 is very equity market negative.
I don’t know which it is, but it is one of the two. I hope it’s the former, but I fear it’s the latter– as I still can’t get it through my head how we all get global economic growth without stimulating massive inflation across the globe. The path out of this multi-year, global economic malaise is through economic growth and inflation—that’s what we should all want to happen—but commodities are telling us it isn’t happening. And, while I hope we’re embarking on an 1980s-style equity bull market, I just can’t see how at this point.
A look at the Most Obvious Trend in the Bond Market
/in Investing/by Tom 2Currencies & Bonds
The “hawkish” Fed minutes were the main driver of trading in both Treasurys and the currency markets yesterday, as the thought of a dial-back of accommodation led to lower Treasury prices and a higher Dollar Index.
Treasurys declined sharply (30-year down 0.77%) and of note the decline accelerated throughout the afternoon despite a decently well-received 10-year Treasury auction that saw a bid to cover in line with recent averages despite the lower yield. But, Fed minutes trumped demand for Treasurys yesterday.
In currencies the Dollar Index rallied 0.3%, and was higher against the euro, pound and yen (which continues to inch closer to 100 yen/dollar).
Looking at the commodity currencies, the Aussie dollar continues its rally, rising to two-month highs in reaction to the stronger Chinese import data (that’s positive for Australian raw material exports).
Steepening Might Be the Most Obviously Trend in the Bond Market
Of note in the bond market yesterday was an article in the WSJ (link here) that focused on the fact that Bill Gross was bullish on the 10-year Treasury, an opinion based solely on the fact that “In this environment, and ever since 2008, an investor needs to buy what central banks buy before (central banks) buy them…..In this case, since its JGB’s, an investor needs to buy what Japanese institutions will buy.”
That logic, I believe, is sound, and this is coming from one of the bigger long-term Treasury bears out there. But, while I agree with Gross’s call on increased demand for 10-year or shorter-duration Treasurys, I still think the trend in the 30-year is lower, so this presents an interesting spread trade idea—Long TBF (I-Shares Short 20+ year Treasury) and also long IEF (I-Shares 7-10 year Treasury). So, you’re short the long end of the curve, and long the “belly” or medium part of the curve.
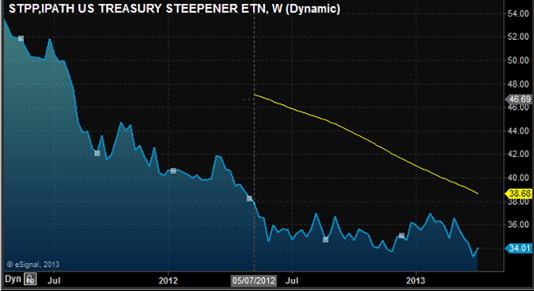
Or, put another way, if we have long dated bonds underperforming while shorter and medium-term bonds are well supported, we should see a significant steepening of the yield curve, and oddly enough there is an ETF for that too: STPP (IPath US Treasury Steepener ETN).
Now, this thing is totally trade by appointment and it’s an ETN, but it’s at pretty much all-time lows—so something to consider as another way to play the bond market where the BOJ is now a major influence.
What to Watch in Economics for the Week Ahead
/in Investing/by Tom 2Economics
This Week
Compared to last week, things will be relatively quiet on the economics front this week. The most important domestic report will be retail sales on Friday. Given the payroll tax hikes, increased healthcare costs and sequester, markets are concerned whether or not the consumer can hold up. So far, the data has shown the consumer is still spending, but the employment report has people nervous, especially after the retail industry dropped 24k jobs in March.
Second in importance this week will be the Fed Minutes from the most recent meeting. The market will be looking for more clarity regarding when QE purchases will be scaled back, although given that the last meeting was an extended one with a press conference and growth projections, I’m not sure there will be much gleaned from the minutes that we don’t already know.
Finally, jobless claims will be watched Thursday, specifically to see if that big Easter-related jump in claims is revised down. Given the soft monthly jobs report last Friday, this will take on even greater significance.
Looking Internationally, by far the most important report this week will be Chinese CPI (released tonight). The main concern in China remains rising inflation, in that it could continue to force additional fiscal tightening from Beijing. Given the stagnation in Europe, the global economy needs China to continue to see growth accelerate, and that will be hard to accomplish if inflation is running too hot.
Things quiet down in Europe this week, as there isn’t a lot of economic data. EMU Industrial Production (Friday) is the highlight, and German IP (today) will also be watched—but those reports, even if they are better than expectations, won’t be enough to stem the growing concern that the EU economy is once again contracting.
Central Bank Decisions
/in Investing/by Tom 2Central Bank Decisions
Bank of Japan
The bar was set pretty high for the BOJ coming into yesterday’s meeting. Investors were expecting a lot of additional monetary easing, but seeing as the yen had already declined significantly, most assumed that the “dovish” results of the meeting were priced in. They were wrong.
New Bank of Japan Governor Kuroda promised earlier in the week to do everything he can to break deflation, and he stuck to his words. Without getting into the weeds of the fiscal details, the Bank of Japan has put its monetary accommodation into overdrive.
- The Bank of Japan is going to specifically try to inflate asset prices (stocks and bonds) by increasing the adjusted monetary base (i.e. printing money) at a pace of 60 to 70 trillion yen annually over the next two years, compared to an increase of 13.4 trillion yen in ’12 and 15.6 trillion yen in ’11.
- Additionally, the BOJ will start buying massive amounts of long-term government bonds (more than doubling the current pace of 20 trillion worth of bonds to 50 trillion).
- Finally, the BOJ will increase the amount of ETFs it is currently buying by 100% (from 500 billion yen to 1 trillion yen).
Takeaway
I’m as big a Japan bull as anyone I know – starting from when I first pointed out the bullish trend emerging last fall with the election of Prime Minister Shinzo Abe. In an investment landscape that is very conflicted and uncertain, the Japan bull market in equities was and is one of the most clear and powerful trends in the market. But, as much of a bull as I was, I never would have dreamed of this type of historically aggressive monetary policy. The bottom line here is that I believe that Japanese stocks are heading much, much higher, and the yen is heading much, much lower. I’ve made the analogy often that buying Japan now is like buying the S&P 500 at the start of the QE program – well now it’s like buying it at the start of a QE program on steroids. Long DXJ remains my top idea in the markets today.
Don’t Forget About the DOW
/in Investing/by Tom 2Interestingly, the Dow was a big outperformer on the day (up .76%), and usually when that happens there is one stock that is up several percentage points that skews the average. Interestingly, that was not the case on Monday, as the strength in the Dow was evenly spread across many of the index components (TRV, The Travelers, was the best performing stock in the index up just 1.79%).
The Dow is now up 5.76% for the year, about half of the S&P 500. The reason for this underperformance has to do with the sectors that have rallied the most year to date (Tech and Financials) which are more heavily weighted in the S&P than in the Dow (plus the Dow doesn’t have AAPL).
But, the outperformance today should be noted. If we are heading into a period of concern/weakness in the markets, the sturdy, somewhat stodgy, industrial companies in the Dow, with strong cash flows, good yields, and decidedly less economically sensitive businesses, will outperform.
If investors are concerned about the market trading like it’s 2011, then perhaps it’s helpful to look at what worked in 2011. Keep in mind, in 2011 the Dow finished up 5.5%, while the S&P was flat, and the NASDAQ fell 1.8%.
Address
4880 Donald Ross Rd., Suite 210
Palm Beach Gardens, FL 33418
info@sevensreport.com
Phone
(561) 408-0918